 |
The Golden Ratio and Sacred Geometry |
| Reload in Frames | Home/Artwork |
Scroll down to learn more about the Golden Ratio, or select from the following topics:
What is Sacred Geometry?To me, sacred means something that is symbolic of a trancendent truth, and worthy of study, contemplation, and veneration. When I refer to Sacred Geometry, I am talking about geometry that is derived from or directly related to the structure of nature. This includes the geometry and numerological mysticism of the Pythagoreans and the alchemists, but also the fractal geometry discovered through science. Our universe is structured in a highly complex yet sublimely ordered manner. This is a truth that is readily felt by sensitive people, and has been demonstrated by science and mathematics. Structural forms seen at the microscopic level are repeated at other scales, and the laws of fractional symmetry appear to apply throughout. So, geometry that refers to the structural unity of nature is a powerful metaphor for the mystery of life, and thus sacred. One of the best examples of Sacred Geometry are forms based on the Golden Ratio.
Knowledge of the Golden Section, ratio, or proportion has been known for a very long time. The Egyptians knew about it and the Greeks learned about it from them. It is called phi, Φ, in honor of Phidias, the architect of the Parthenon, and is approximated by the irrational fraction 0.618034... Shamans, priests, and artists throughout the world and across history have understood and applied Φ to ritual, architecture, art, and the crafting of musical instruments and everyday objects.
Φ shows up throughout nature and represents one of the most fundamental numerical constants of the universe. Recall Vitruvian Man, a drawing by Leonardo showing man within the circle and the Golden Ratios in the human body. Le Corbusier's The Modular represents a more recent study of the Golden Ratio in the human form. For example, the finger bones are in approximate Φ ratio to each other, and the position of features on the human face is related to Φ. The major 6th harmony interval in music is in Φ ratio to the octave.
The Golden Rectangle (GR), the organizing form in my current art work, is a rectangle with a short to long side ratio of 1: 1.618..., or 1: (1 + Φ). An interesting property of GR's is that if you cut out a square starting from one of the short sides of the GR, you will be left with another GR. You can continue to cut out short side squares for each successively smaller GR and another smaller GR will remain. And the dimensions of each successively smaller rectangle will be in Φ ratio to the previous larger size. A series of my collage explore this Φ-ratio "coiling" property of GR's, seen here in Figure 1:
Figure 1 - A Golden Rectangle that has been subdivided into short-side squares that create proportionally smaller Golden Rectangles. |
|
| 1 |
Figure 2 shows a logarithmic spiral superimposed on a coiled GR. This study shows the Φ-ratio sectioning of the GR with short side squares and the diagonals of the original seed GR (GR0) - outside boundary lines) and the diagonal of the first Φ-sectioned GR (GR1). Note that the two diagonals intersect at a point mathematician Clifford Pickover called the "Eye of God," the origin of the logarithmic spiral.
Figure 2 - The logarithmic spiral fits within coiled golden rectangles and converges on a point Clifford Pickover called the Eye of God. The Eye of God is also defined by the intersection of the diagonals for GR0 and the diagonals for the two symmetric GR1s. |
|
|
|
Logarithmic spirals are natural forms and many other natural forms fit neatly within a GR. Examples include bird eggs, human heads, and spruce trees. So, it would seem that the distinction between a simple "geometric" form like a GR and an "organic" form like a logarithmic spiral is superficial. Both forms imply and can be derived from the other!
The symmetry of GR's means that the coiling can proceed in 4 different ways, explored in Figure 3. Here we can see that there are implied diagonal lines (gray) and shapes within a GR - and that the four Eyes of God within a GR imply another smaller GR (in the middle). The sides of the inner "Eyes of God" GR have a special ratio to the sides of GR0 - it has length and width that are in square-root of 5 (√5 = 2.236...) ratio (1: 2.236...) to the larger GR0 sides. The irrational number √5, appears often, both in the calculation of Φ (see below) and when GR forms are combined.
Figure 3 - Diagonals within a GR intersecting at the four "Eyes of God" form the corners of another GR (central orange GR) in √5 ratio to the original GR sides. Vertical lines through the Eyes of God also create 2 √5 rectangles (green vertical rectangles). |
|
|
|
Figure 4 shows the √5 rectangle that is composed of overlapping GR's that share a central square. This rectangle was a favorite form of the ancient Greeks for architectural features and everyday objects, and I have used it frequently as a collage form. This wider √5 rectangle is in the aspect ratio of 1: (2.236...).
Figure 4 - The √5 rectangle formed by two GRs that share a central square used as collage form. This is a recent collage from the Abstract √5 Series: Collage 2016-006, ©2016 Doug Craft. |
|
|
A final note about the GR involves fractals. Fractals are geometric forms that look the same no matter what the size scale. They are composed of repeating units that combine to make larger and similar units at larger scales. This property is called self-similarity, and it is also a fundamental property of nature and natural forms. Fractals also have a property called fractional dimension, which means that printed images of fractals have a dimension in between 1 (a line) and 2 dimensions (a plane). The coiled GR shows self similarity - smaller squares and GRs are the self-similar shapes that are repeated. A coiled GR is fractal-like with respect to self similarity, but it does not have fractional dimension. All of the abstract images in my collages also contain fractal form elements. For example, clouds, coastlines,landscapes, and rock have fractal structure.
There are 2 general ways to derive Φ. One approach uses the Fibonacci numbers, and the other is geometrical and algebraic. Fibonacci numbers are easier to comprehend, so let's start there.
Fibonacci was the pen name of Leonardo of Pisa, a 13th century mathematician whose book, Liber Abaci, introduced western civilization to Arabic/Hindu numerals (replacing Roman numerals), and a special sequence of numbers named after him. Fibonacci raised rabbits and observed their population numbers over successive generations. They increased in a peculiar "additive" way, and from this he surmised the more abstract number sequence. Starting with 0 and 1 as the first two numbers in the sequence (or 1 and 1), each successive number is determined by adding the previous two numbers. Starting with 0 and 1, the series goes like this:
It turns out that this sequence of integers appears widely in nature, and is observed in the dimensions and leaf branching (phyllotaxis)of plants, animals, as well as crystals. This happens when things grow because the new growth often occurs on top of an existing structure - like new branches on a tree, or offspring added to a tribe. Many plants exhibit Fibonacci numbers in branching, and in spiral structures like the arrangement of rows of bracts on pinecones, petals on an artichoke, and scales on a pineapple.
This would just be a curiosity about growing things until we start calculating the ratio between adjacent Fibonacci numbers. Table 1 lists the Fibonacci numbers in the left column, the ratio calculations in the middle column, and the results in the right column. It turns out that after the fifth Fibonacci number, the ratio begins to get very close to the algebraic solution for Φ = 0.6180339... If you figure that two decimal places are as much as even the most careful craftsman can measure and cut, then the 6th Fibonacci ratio, 8 ÷ 13, will do as an approximation of 0.62 for Φ. After the 16th Fibonacci number, the ratio approximates Φ to 6 decimal places. Higher Fibonacci number ratios yield changes in only in the 7th decimal place and beyond.
Fibonacci number |
Ratio Calculation |
Result |
Fibonacci number |
Ratio Calculation |
Result |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
55 |
34 ÷ 55 |
0.618181 |
|||
1 |
1 ÷ 1 |
1.000000 |
89 |
55 ÷ 89 |
0.617977 |
|
2 |
1 ÷ 2 |
0.500000 |
144 |
89 ÷ 144 |
0.618055 |
|
3 |
2 ÷ 3 |
0.666666 |
233 |
144 ÷ 233 |
0.618025 |
|
5 |
3 ÷ 5 |
0.600000 |
377 |
233 ÷ 377 |
0.618037 |
|
8 |
5 ÷ 8 |
0.625000 |
610 |
377 ÷ 610 |
0.618032 |
|
13 |
8 ÷ 13 |
0.615384 |
987 |
610 ÷ 987 |
0.618034 |
|
21 |
13 ÷ 21 |
0.619047 |
1,597 |
987 ÷ 1,597 |
0.618033 |
|
34 |
21 ÷ 34 |
0.617647 |
2,584 |
1,597 ÷ 2,584 |
0.618034 |
So, Fibonacci numbers are related to Φ and can be used to derive the Golden Ratio. I use frame dimensions of 21" x 13" for coiled GR collages (Figure 1) which are adjacent Fibonacci numbers. Saves a lot of trouble trying to get precise odd fractions of an inch cuts using the matte cutter!
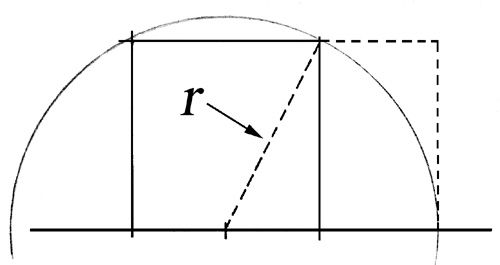
The geometric approach to drawing a GR is fairly simple using a straightedge and compass. Refer to Figure 5. Basically, draw a straight base line across the bottom of a sheet. Draw a fairly large square near the middle of the line segment. Make sure the sides are perpendicular and equal. Find the midpoint of the bottom side of the square and mark it. Take the compass and stick the sharp point at the midpoint of the bottom of the square. With the compass point at the marked midpoint, open the compass until the pencil point touches the upper right hand corner of the square, radius r in figure 5. Now draw a big half-circle that intersects the baseline. Draw a line extending the square and a perpendicular line that meets the point where the big circle intersected the baseline. You have created a Golden Rectangle!
Figure 5 - Creating a Golden Rectangle using a compass and straightedge. |
|
|
For the algebraic method (which can be skipped if you are not mathematically inclined), consider the geometric definition of Φ on a line segment, AB, seen in Figure 6. We want to find the Golden Section: the point on AB, call it C, such that the ratio of the big chunk AC to the whole segment AB is the same as the ratio of the small chunk, CB, to the big chunk, AC. For C to be the Golden Section point, (AC divided by AB) must equal (CB divided by AC).
|<----------------AB------------------>| A C B ._______________________.______________. |<----------AC--------->|<-----CB----->| |
To simplify matters (or to confuse the less mathematically gifted), we will do some substitutions. Here's how: Let's say the whole segment AB = 1, and we will let AC be phi, Φ. Now, it should be clear that the whole segment AB is the sum of the 2 parts, AC and CB, right? So we can set up an equation that says the same thing:
AB
= AC + CB |
AB
- AC = CB |
1
- Φ = CB |
Figure 7 shows how the substitutions have changed the problem. Here we show the line segments with the new substituted terms.
|<---------------- 1 ----------------->| A C B ._______________________.______________. |<--------- Φ --------->|<--(1- -Φ)--->| |
With me so far? OK...now we are going to set up an algebraic equation to solve for Φ. Remember our definition: for C to be the Golden Section of segment AB, the ratio of the big chunk AC to the whole segment AB, has got to be the same as the ratio of the little chunk CB to the big chunk AC. So now we can set this up as an equation:
| Eq.1 |  |
| Eq.2 | 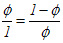 |
| Eq.3 | 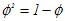 |
| Eq.4 | 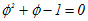 |
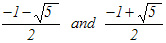 |
These books have been helpful in my study of the Golden Proportion and form in nature and art. I recommend Garland's Fascinating Fibonaccis to anyone who would like a general overview. It's easy to understand and gives a lot of good visual examples. Teachers may want to consider Garland as an introduction and Runion's The Golden Section for a more math-oriented approach with problems in each chapter. Garland is suitable for middle school kids while Runion is high school algebra level. Let me know if you have recommendations for other books on the subject of sacred geometry, the Golden Ratio, or form-based aesthetics.
Bak, Per, 1996. How Nature Works - The Science of Self-Organized Criticality, Springer-Verlag, New York.